If your community needs to establish Long-Term Services and Supports or improve its current program, the LTSS roadmap planning model can guide you through the planning process. This roadmap will help you understand your community’s needs and work toward meeting them — whether you have an active program already or are beginning the planning process for the first time.
The Roadmap Model
The roadmap offers a step-by-step planning process for addressing LTSS needs in your tribal community. It will help you plan strategically by considering LTSS needs, resources for services, and opportunities for collaboration. This model will show you the necessary steps to build an LTSS program that fits your community.
Step 1. Needs Assessment
A needs assessment involves gathering information to understand different aspects of your community, including demographics, community needs, and available strengths and resources. This assessment helps pinpoint the most crucial needs in your community, reducing the risk of investing in unnecessary services. Expert guidance can ensure accurate results.
Watch the video below to learn about the Menominee Indian Tribe of Wisconsin’s model of long-term care and see an example of how the tribe conducted a needs assessment:
The process typically involves several steps:
Identify Initial Needs: Determine the community’s problems and needs, which will serve as a benchmark for measuring progress.
Define Problems: Identify specific services needed and potential obstacles to implementing them. Sample problems could include the lack of home- and community-based care, caregiver training, budget-friendly care models, staff shortages, funding shortages, and space limitations.
Identify Stakeholders: These are individuals or organizations directly affected by or interested in the planning process, such as tribal leaders, elders, caregivers, healthcare providers, and relevant nonprofits.
Collect Data: Gather data through interviews, surveys, focus groups, and reviewing existing reports or research. Data sources can include census data, clinic records, economic profiles, and health records.
Organize and Study Data: Analyze the collected data to gain insights into the community’s needs.
Define LTSS Needs: Evaluate the gathered information to understand the community’s LTSS needs, considering both expected and unexpected issues.
Describe LTSS Needs: Identify who requires LTSS services, including demographics, disabilities, and location. Assess available services and gaps to develop a plan for building necessary services, such as transportation or caregiver respite.
Step 2. Goals and Objectives
Setting goals for your community’s LTSS program helps clarify your purpose and identify the issues you want to address. Objectives are specific targets that support your goals, while performance benchmark help measure progress toward achieving them.
To identify LTSS goals and objectives:
Begin by asking:
What goals do you want to achieve through your LTSS program?
- Example: “I want to provide reservation-based home health care services.”
- What specific objectives do you need to accomplish to reach these goals?
- Example: “I need to learn about state accreditation for home health care services.”
Clearly define your goals and objectives:
- Example goal: “Improve the quality of life for our elders and people with disabilities.”
- Example objective: “Achieve 100 percent Medicaid enrollment among eligible community members by June 30, 2027.”
Choose performance benchmarks:
- Performance benchmarks are measurable statistics used to track change.
- Consider benchmarks such as Medicaid enrollment rates, number of mental health screenings, and hospital re-admittance rates.
- Refer to established indicators like those outlined in the “Older Americans 2016: Key Indicators of Well-Being” report for additional guidance.
Once you have identified LTSS goals, objectives, and performance benchmarks, compare different LTSS models to find one that aligns with your community’s needs.
Step 3. Compare Models
Now, it’s time to start selecting the right LTSS model for your community. This involves looking at the available options and determining which model would best suit your community’s needs.
There are two main LTSS models:
- Home- and Community-Based Services: This provides personalized care at home or in community settings.
- Facility-Based Services: Care is given in institutions like assisted living residences, adult family homes, or nursing homes.
At this stage, it’s crucial to consider the financial aspects and the level of tribal involvement:
Financial Considerations:
- Financing and reimbursement options vary from state to state.
- Different Medicaid programs may offer different reimbursement opportunities.
- Explore creating a budget and financing plan, as well as understanding different funding sources and reimbursement rates.
Level of Tribal Involvement:
- Tribes can support LTSS programs through executive and legislative backing, governance, program management, and related program support.
- Different models require varying levels and types of tribal involvement.
- Assess how your tribe can assist in areas such as direct services, management structure, costs, and program sustainability.
After reviewing the available LTSS models and considering financial factors and tribal involvement, choose the model that best aligns with your community’s needs.
Step 4. Select Model
To effectively implement LTSS in your community, consider various factors:
Community Relevance: Analyze available LTSS models to ensure alignment with your community’s needs. Assess impact, required resources, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
Required Resources (Non-Financial): Determine if your tribe possesses sufficient human resources and technical expertise. Understand state regulations and best practices to identify necessary non-financial resources, such as:
- Expertise in relevant areas
- Access to broadband internet, electronic health records, cell phones, and diagnostic equipment
Implementation Needs: Assess requirements like licensure, insurance, building, equipment, personnel, staff housing, and transportation for staff or clients.
State Policies and Reimbursement: Understand your state’s policies regarding LTSS and reimbursement, including quality standards and which services are eligible for Medicaid reimbursement.
Sustainability and Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate whether your chosen model can serve enough people to be financially viable. Compare the costs and level of care of different models and conduct a break-even analysis.
SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis to assess Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Consider internal factors like staff qualifications and external factors like state funding changes. This analysis helps in planning and adapting your LTSS program effectively.
By considering these factors and conducting thorough assessments, you can select and implement the most suitable LTSS model for your community’s needs.
Step 5. Planning
Once you’ve chosen your LTSS model, it’s crucial to consider how its implementation will be influenced by various factors in community health planning and care. Strategic planning helps anticipate problems, assess your community’s current situation, and leverage its strengths. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the strategic planning process:
Understand Your LTSS Model:
- Review program requirements, including financing, certification, and staffing.
- Identify funding sources for program creation or improvement, as well as ongoing costs.
- Review certification requirements from third-party payers like Medicaid.
- Determine the financial support your tribe can provide.
Plan Strategically:
- Identify potential factors impacting your program.
- Use insights from SWOT analysis to inform strategic planning, updating as needed.
- Determine if tribal protocols require additional actions, such as conducting a needs assessment.
- Develop action items based on your analysis.
- Explore opportunities to optimize resources, like sharing overhead costs with existing tribal clinics.
Watch the video below to learn more about leveraging resources and how to maximize resources you already have.
Prepare for Implementation:
- Create an implementation plan with timelines for each task.
- Mobilize internal and external resources.
- Prioritize action items from your SWOT analysis.
- Address tribal protocols or processes, such as revising codes for elder abuse.
- Establish necessary agreements, like Memorandums of Understanding with state agencies.
- Engage key contacts within your tribe and broader community.
- Review current and future needs regarding training and funding, seeking collaborative solutions.
Once you’ve crafted a comprehensive plan and addressed internal and external considerations, your LTSS implementation plan is ready to be executed.
Step 6. Implementation
Implementation Checklist
The steps taken in previous stages should have helped outline the necessary actions for implementing your chosen LTSS model in your community. This checklist can provide clarity on specific aspects of your program. Depending on your plan, you may want to customize this list or break down items into smaller steps.
Financing:
- Ensure your program can bill for services.
- Review and update billing codes.
- Determine if a tribal resolution is needed for billing changes.
- Discuss funding options with your tribe, including budget allocations.
- Negotiate reimbursement rates with state Medicaid officials.
Buildings:
- Collaborate with your tribe to secure space for building, renovating, or leasing.
Accreditation:
- Meet requirements of accrediting agencies.
- Identify the necessary accreditation agency based on your facility type.
- Take steps to fulfill accreditation requirements.
- Submit applications for gaining or renewing accreditation.
Staffing:
- Recruit, hire, and train staff as needed.
- Ensure staff meet required certifications for accreditation.
- Establish contact with external providers for potential contracts.
Program Development Resources:
- Utilize national organizations specializing in tribal LTSS programs.
- Explore initiatives tailored for tribal cooperation.
Certification for Medicare and Medicaid:
- Pursue certification through CMS for Medicare and Medicaid, which is crucial for LTSS programs.
- Allocate ample time for the certification and accreditation process.
Create a Work Plan:
Develop a comprehensive work plan outlining activities and timelines.
Sample Work Plan:
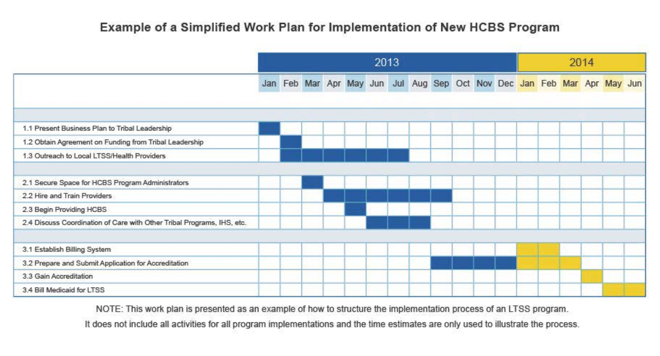
Strategies for Success:
- Leverage existing resources.
- Integrate LTSS services with existing tribal health programs.
- Collaborate with similar programs in other tribes.
- Establish or enhance elder safety codes and task forces.
- Maintain regular communication with stakeholders.
- Recruit LTSS champions to build support and momentum.
- Secure backing from tribal leaders and the community.
- Form partnerships with tribal and non-tribal providers.
After implementation, evaluate the effectiveness of your LTSS program in achieving its goals and benefiting community members. Regular assessments ensure ongoing improvement and alignment with community needs.
Step 7. Evaluation
After establishing or modifying a LTSS program, assessing its impact becomes crucial. Evaluation helps gauge progress, identify successes, and pinpoint areas for improvement.
Evaluation Questions:
- Comparative Progress: How do current outcomes compare to initial baseline measurements?
- Objective Achievement: Has the program met its set objectives?
- Goal Attainment: Has the program achieved its overarching goal?
- Sustainability: Is the program viable in the long run?
- Financial Considerations: Have program costs changed, and is revenue covering operational expenses?
- Growth Opportunities: Are there chances for service expansion or maintenance?
Key Evaluation Elements:
- Utilize performance benchmarks from Step 2 to track measurable results regularly.
- Assess changes in program participation and service delivery over time.
- Evaluate effectiveness, efficiency, and impact on key indicators such as elders’ health outcomes and collaboration levels.
- Analyze how resource utilization correlates with LTSS outcomes and compare the effectiveness of different services.
- Learn from both achieved and unmet objectives to refine program performance and adapt objectives accordingly.
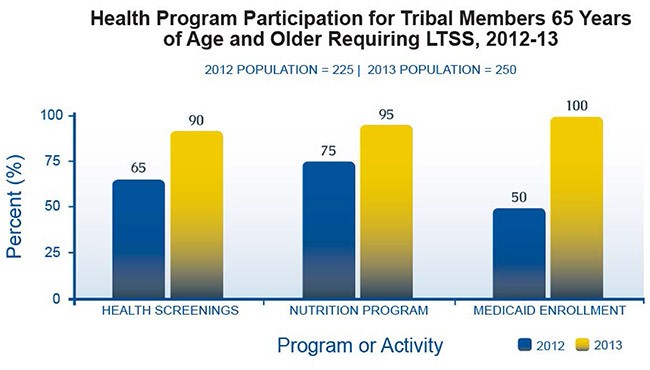
Program Participation Over Time
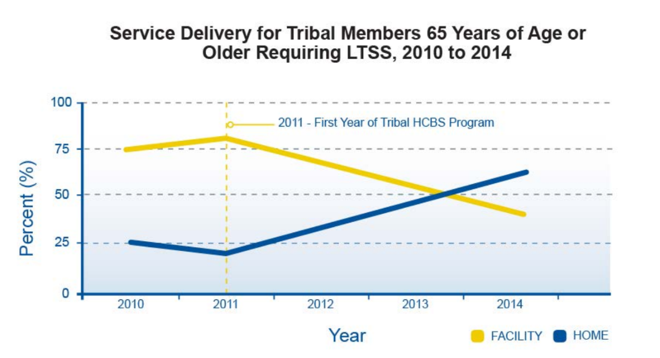
Services Delivered by Different Program Types Over Time
Logic Model:
- Develop a logic model outlining resources, activities, outputs, and short- and long-term outcomes.
- This model provides a structured framework for organizing evaluation findings.
The model provides a structured way of organizing the information you discover from your evaluation.
Example of CoC Logic Model
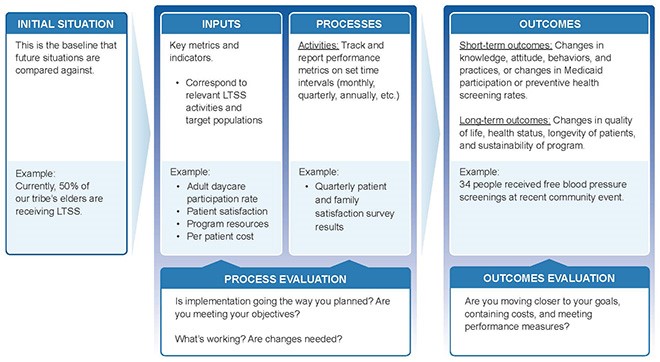
Resources
Here are some resources for your reference:
- Resources by State
- Find Continuum of Care Services (nicoacompass.org)
- Medicaid State Fact Sheets (KFF)
- https://www.kff.org/interactive/medicaid-state-fact-sheets/
- 10 Things About Long-Term Services and Supports (LTSS)
- https://www.kff.org/medicaid/issue-brief/10-things-about-long-term-services-and-supports-ltss/
- Who Uses Medicaid Long-Term Services and Supports?
- https://www.kff.org/medicaid/issue-brief/who-uses-medicaid-long-term-services-and-supports/
- Dying Broke A KFF Health News-New York Times Project
- https://kffhealthnews.org/dying-broke/
All content on this page was originally posted on the CMS.gov website.
